Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kunimaru, Takanori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1185 - 1194, 2011/09
This study will be demonstrated the selection process for the URL area and URL site in sequence. Horonobe URL has been declared to be constructed within whole Horonobe Town to be selected early in the fiscal year 2002. The Horonobe URL area/site is required existence of host argillaceous sedimentary formations and saline groundwater. Further fundamental requirements are rock mechanical property and underground flammable (e.g. methane) gas content which meet with safe construction and operation of underground facility. Next, based on surveys of existing information and aerial and ground reconnaissance surveys on a regional scale, and taking into consideration preliminary requirements on the geological environment and safety, as well as social and environmental constraints, an area of 3 km  3 km in the north-central part of Horonobe Town was selected as the main area for the surface-based investigations (URL area). A site for constructing the underground and surface facilities (URL site) was subsequently selected in the URL area, 3 km from the center of Horonobe Town. The selection was based on social conditions and the availability of infrastructure, including roads and land use restrictions, in addition to available geological and hydrogeological information. This study is only fruit of selecting the URL site based on the social and technical requirements in Japan. These stepwise approaches and experiences for selecting the site are applicable when the implementer (e.g. Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan) will select the site such as the phase of literature survey, preliminary investigation and detailed investigation in the future.
3 km in the north-central part of Horonobe Town was selected as the main area for the surface-based investigations (URL area). A site for constructing the underground and surface facilities (URL site) was subsequently selected in the URL area, 3 km from the center of Horonobe Town. The selection was based on social conditions and the availability of infrastructure, including roads and land use restrictions, in addition to available geological and hydrogeological information. This study is only fruit of selecting the URL site based on the social and technical requirements in Japan. These stepwise approaches and experiences for selecting the site are applicable when the implementer (e.g. Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan) will select the site such as the phase of literature survey, preliminary investigation and detailed investigation in the future.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Onoe, Hironori; Doke, Ryosuke
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1451 - 1460, 2011/09
The site descriptive modeling, which includes modeling of geological characteristics at present and modeling of site evolution, is used for synthesis of investigation results. It is important to evaluate uncertainties in the model, to specify issues regarding the uncertainties, and to prioritize the specified issues, for the planning of site characterization. The aim of this study is to support for the planning of initial surface-based site characterization based on the technical know-how accumulated from the JAEA's Underground Research Laboratory Projects. In this study, comprehensive task flow from pre-existing data acquisition to site characterization planning through the modeling has been specified. Specific task flow and decision-making process to perform the tasks have been specified, and decision points have also been identified.
Doke, Ryosuke; Yasue, Kenichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakayasu, Akio
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1467 - 1476, 2011/09
Palaeo-hydrogeological information based on reconstructing topographical evolution for disposal sites is considered to be available to build a predictive repository safety assessment. However, the construction of the topographical evolution models has a complicated and tacit working process. Additionally, in the investigation and modeling of topographical evolution for site characterization, it is important to make available the technical know-how (e.g., decision-making process) accumulated over decades of research and development and to transfer the knowledge during initiation and implementation phase. The aim of this study is to externalize the technical know-how for the construction of the topographical evolution models. The working process of the model construction is illustrated as a "task-flow" including the tasks of setting of time scale, extraction of information, construction of conceptual model and construction of numerical model. In each task, explanations with the information of input and output data are described in detail. The linkages with other task-flows, such as the investigations and other modeling, were also described in the task-flow. Additionally, the decision-making processes in the investigations are expressed as IF-THEN format in flow-diagrams for each task. Accordingly, IT-based expert systems including the externalized technical know-how are constructed to support planning and implementation of the investigations and modeling for topographical evolution.
Amano, Kenji; Niizato, Tadafumi; Ota, Kunio; Lanyon, B.*; Alexander, W. R.*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1477 - 1481, 2011/09
The assurance of the long-term stability of the geological environment is  for deep geological disposal. In Japan, since uplift/subsidence and climatic and sea-level changes would result in a significant change to hydraulic and hydrochemical conditions at coastal sites, it is of importance to establish comprehensive techniques for characterising the overall evolution of coastal sites over geological time. To this end, modelling techniques focussing on the coastal site evolution have been developed through the collaborative research programme at the Horonobe coastal study area. A palaeohydrogeological conceptual model has been developed based on all available information and eventually key geological properties and processes as well as a methodology for appropriately defining the initial and boundary conditions for long-term groundwater flow simulations have been clarified.
for deep geological disposal. In Japan, since uplift/subsidence and climatic and sea-level changes would result in a significant change to hydraulic and hydrochemical conditions at coastal sites, it is of importance to establish comprehensive techniques for characterising the overall evolution of coastal sites over geological time. To this end, modelling techniques focussing on the coastal site evolution have been developed through the collaborative research programme at the Horonobe coastal study area. A palaeohydrogeological conceptual model has been developed based on all available information and eventually key geological properties and processes as well as a methodology for appropriately defining the initial and boundary conditions for long-term groundwater flow simulations have been clarified.
 gas
gasHata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.105 - 110, 2011/09
IF treatment technique belongs to the system decontamination technology. It has the high performance decontamination technique for the plant that deposits the uranium intermediate fluoride, for example, UF
treatment technique belongs to the system decontamination technology. It has the high performance decontamination technique for the plant that deposits the uranium intermediate fluoride, for example, UF , UF
, UF , U
, U F
F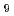 , and U
, and U F
F , which exist in the uranium enrichment plant by the Gas Centrifuge. The characteristics of IF
, which exist in the uranium enrichment plant by the Gas Centrifuge. The characteristics of IF treatment, the secondary waste is just an IF
treatment, the secondary waste is just an IF and little adsorbent. In addition, this IF
and little adsorbent. In addition, this IF is possible to reuse as a materials for makings new IF
is possible to reuse as a materials for makings new IF gas. According to that IF
gas. According to that IF treatment is the simple method using chemical reaction, we hardly need to care about secondary reaction with the exception of the reaction with IF
treatment is the simple method using chemical reaction, we hardly need to care about secondary reaction with the exception of the reaction with IF gas and the uranium intermediate fluoride. This is very important feature when applying to a large-scale plant.
gas and the uranium intermediate fluoride. This is very important feature when applying to a large-scale plant.
Haraga, Tomoko; Nakano, Yuta*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Saito, Shingo*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1461 - 1465, 2011/09
Actinides are important nuclides for the analysis of radioactive wastes from nuclear fuel cycle facilities. In order to achieve simple and rapid analysis of actinides, capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescent detection method (CE-LIF) is one of the potential candidates. In this study, new emissive probes of actinide ions suitable for CE-LIF were developed for the first time. The detection and separation of americium and neptunium ions as model nuclides were examined using several new emissive complexing probes, each of which possessed a fluorophore and a different chelating moiety. Using acyclic and macrocyclic multidentate probes, the highly sensitive fluorescent detection of Am and Np was successfully achieved. The results suggests that the probe with an acyclic hexadentate chelating moiety is suitable for detection and separation of Am and Np. The detection limit of mid-ppt levels was determined.
Asai, Shiho; Okumura, Keisuke; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Suzuki, Hideya; Toshimitsu, Masaaki; Inagawa, Jun; Kimura, Takaumi; Kaneko, Satoru*; Suzuki, Kensuke*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1437 - 1442, 2011/09
Okumura, Keisuke; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Suzuki, Hideya; Toshimitsu, Masaaki; Inagawa, Jun; Kimura, Takaumi; Suzuki, Kensuke*; Kaneko, Satoru*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1443 - 1450, 2011/09
Inventory estimation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) in high-level radioactive wastes (HLW) from spent nuclear fuels of light water reactors is important for a safety assessment of their disposal. In order to develop an inventory estimation method of difficult-to-measure LLFPs (Se-79, Tc-99, Sn-126, and Cs-135), a parametric study was carried out by using a sophisticated burnup calculation code and data. In the parametric study, fuel specifications and irradiation conditions are changed in the conceivable range. The considered parameters are fuel assembly types (PWR / BWR), U-235 enrichment, moderator temperature, void fraction, power density, and so on. From the calculated results, we clarify the burnup characteristics of the target LLFPs and their possible ranges of generations. Finally, candidates of the key nuclide are proposed for the scaling factor method of HLW.